
[ad_1]
Globally, dangerous alcohol use is a causal issue in additional than 200 ailments and accidents and is chargeable for 3 million deaths yearly (WHO, 2022). One strategy to lowering the burden of dangerous alcohol use is to implement population-based screening and transient intervention programmes targeted on stopping unhealthy alcohol use.
Major care interventions characterize a frontline alternative to establish dangers and supply transient recommendation. Supporting proof means that major care transient intervention trials considerably scale back alcohol consumption (Beyer et al., 2018). Equally, proof from randomised managed trials has proven major care administration of Alcohol Use Dysfunction (AUD) is efficient at lowering heavy consuming (Anton et al, 2006).
Nevertheless, while major care settings supply the chance for low-cost alcohol screening and transient intervention and remedy of AUD, they’re scarcely adopted in apply. Regardless of a robust proof base for population-based major care prevention and remedy of alcohol-related issues, many people at-risk from unhealthy and dangerous alcohol use don’t obtain the help they want.
This research (Lee et al., 2023) stories on the Sustained Affected person-Centred Alcohol-Associated Care (SPARC) trial, a randomised implementation trial geared toward enhancing population-level alcohol hurt prevention and AUD remedy throughout major care practices within the US.
The trial aimed to analyze the place the SPARC intervention, in comparison with ordinary care, elevated the proportion of major care sufferers who screened constructive for dangerous alcohol use and acquired a short intervention. Secondly, the trial examined whether or not the SPARC intervention elevated the proportion of major care sufferers who have been newly identified with AUD and acquired AUD remedy.
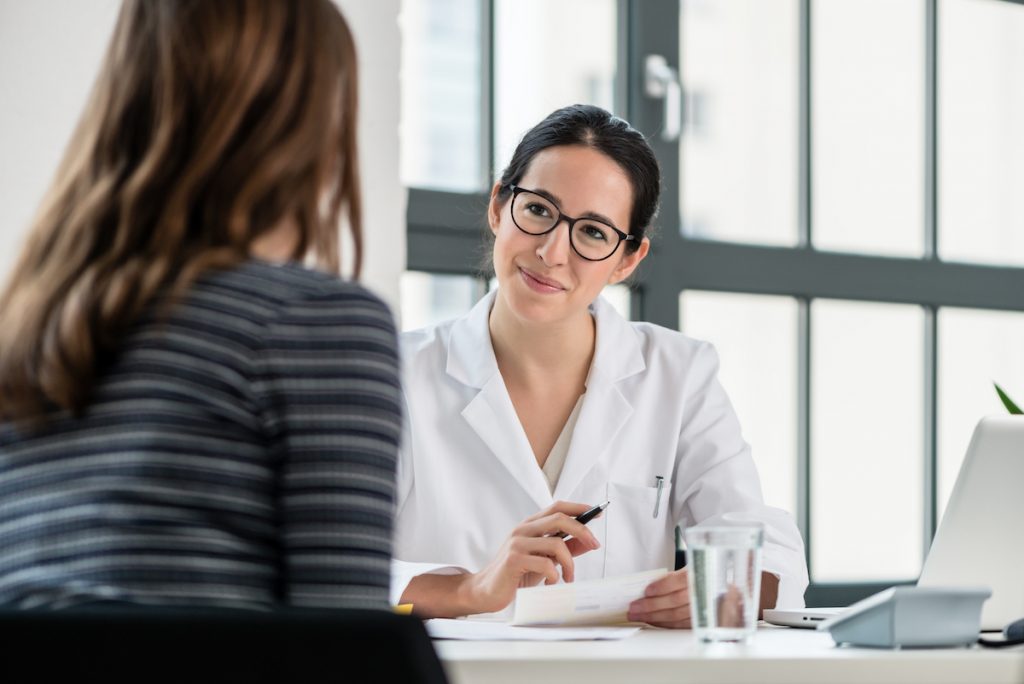

Regardless of the proof for population-based prevention and remedy interventions lowering alcohol use, they aren’t usually carried out in major care.
Strategies
Research design
In a stepped-wedge, cluster randomised implementation trial, 25 major care practices in Washington State, US (with no prior population-based alcohol screening, transient intervention, and AUD analysis and remedy) have been included.
Implementation of the SPARC intervention was a part of a broader programme of behavioural well being together with screening and addressing despair, suicidality and different drug use. Every apply within the research was randomly assigned a begin date, with research waves staggered by 4 months. Months earlier than the trial have been labelled “ordinary care” and people after “SPARC intervention” durations.
Contributors
All sufferers have been at the least 18 years outdated with a go to to major care between January 1st, 2015, and July 31st, 2018, and knowledge have been extracted from Digital Well being Data (EHR) and insurance coverage claims.
Intervention
The SPARC intervention was designed to implement population-based strategy:
- Alcohol screening with the Alcohol Use Problems Identification Take a look at Consumption (AUDIT-C)
- Temporary intervention for sufferers who screened constructive (AUDIT-C ≥ 3 for females and ≥ 4 for males)
- Evaluation with an alcohol symptom guidelines for (DSM-5) AUD for sufferers with high-risk consuming AUDIT-C ≥ 7
- Shared decision-making about AUD remedy choices
- Assist for initiation and engagement in AUD remedy.
The intervention used three evidence-based implementation methods:
- Efficiency suggestions (weekly reporting on the prevalence and evaluation of AUD signs)
- Observe facilitators (experience in alcohol-related care, addressed stigma, inspired patient-centred decision-making for AUD, coaching on behavioural well being integration)
- EHR medical choice help (EHR prompts for screening evaluation for AUD signs and remedy initiation).
Consequence measures
The first consequence for prevention was the presence of each a constructive alcohol display on the day of a major care go to or through the previous 12 months and EHR documentation of transient intervention within the subsequent 14 days. Temporary intervention was indicated by 1 or extra EHR data (together with analysis codes for transient interventions, transient intervention templates and orders for leaflets on unhealthy alcohol use).
The first consequence for AUD remedy engagement was each a brand new AUD analysis on the day of a major care go to (with no analysis within the earlier 12 months) and follow-up in-person remedy initiation and engagement. Initiation required an ICD code inside 14 days after AUD diagnoses, and engagement required 2 or extra visits with ICD codes inside 30 days of initiation.
Secondary outcomes included AUDIT-C constructive screens, excessive constructive screens that prompted evaluation with Alcohol Symptom Guidelines, completion of Alcohol Symptom Guidelines, new AUD analysis and AUD remedy initiation.
Outcomes
Pattern
- Contributors have been 333,596 major care sufferers, with a imply age of 48 years and predominantly feminine (58%) and white (70%)
- 255,789 sufferers have been seen throughout ordinary care versus 228,258 through the SPARC trial.
Prevention and transient intervention
- The proportion of sufferers with a short intervention within the EHR (Digital Well being File) was higher through the SPARC trial in contrast with ordinary care (p < 0.001)
- The proportion of sufferers with documented alcohol screening (p < 0.001) and a constructive alcohol display (p < 0.001) have been additionally higher through the SPARC trial in contrast with ordinary care.
AUD remedy initiation and engagement
- The proportion of sufferers with AUD engagement didn’t differ between the SPARC trial and ordinary care durations (p = 0.30)
- The proportion of sufferers assessed with an Alcohol Symptom Guidelines (p < 0.001), who had a brand new AUD analysis documented (p = 0.003) and initiation of AUD remedy (p = 0.04) was higher through the SPARC trial in comparison with ordinary care.

Sustained Affected person-Centred Alcohol-Associated Care (SPARC) elevated the variety of sufferers who acquired transient intervention for unhealthy alcohol use.
Conclusions
Findings point out {that a} population-based major care trial elevated the prevention of unhealthy alcohol use through mechanisms of elevated alcohol screening and constructive alcohol screens and a higher proportion of transient interventions.
The trial didn’t improve AUD remedy engagement, however did improve key markers within the AUD remedy pathway, together with new AUD diagnoses and initiations of AUD remedy.
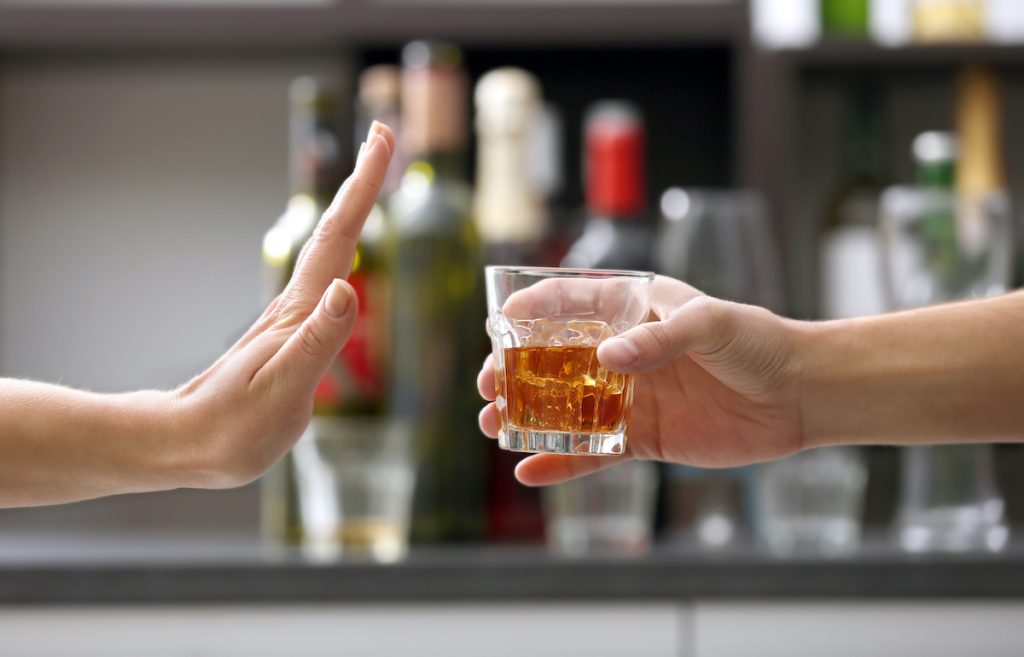

A sensible and low-cost intervention evaluated within the US elevated alcohol prevention care, however not AUD remedy engagement.
Strengths and limitations
SPARC is the primary implementation trial to extend transient intervention, AUD analysis and initiation of AUD remedy in major care with out using research-supported clinicians.
These findings show that population-based implementation trials can enhance prevention and remedy outcomes for dangerous alcohol use outdoors of the carefully managed parameters of medical trial settings. Nevertheless, the magnitude of the will increase briefly interventions, AUD analysis and initiation of remedy are modest. This discovering is per different implementation trials in major care settings that report modest prevention and remedy results. It additionally stays unknown whether or not these results are sustained over time.
The SPARC trial goes past the standard use of EHR as an implementation technique to incorporate efficiency suggestions and apply facilitation. These instruments have been proven to be efficient in supporting major care clinicians to incorporate screening and transient intervention of their apply (Fleming et al, 2004). Nevertheless, given the wide selection of intervention parts and implementation buildings used within the current, it’s troublesome to find out that are handiest in supporting the prevention and remedy of AUD.

This research is an efficient instance of how population-based implementation trials can enhance the prevention of dangerous alcohol use outdoors a managed surroundings.
Implications for apply
Regardless of the introduced proof for low-cost, population-based implementation of prevention of dangerous alcohol use and remedy of AUD, these practices are not often utilized in major care. In a UK-based survey, just one in ten heavy drinkers reported receiving transient recommendation about their consuming in a major care setting (Brown et al, 2016).
Due to this fact, the success of screening, transient intervention, and initiation of AUD remedy depends on their utilisation in major care apply. A number of research have reported on the challenges dealing with major care clinicians in implementing prevention and remedy approaches together with, lack of coaching (Aira et al, 2003) and emotional and ethical difficulties in elevating and assessing alcohol-related issues in consultations (Rapley et al, 2006).
The current findings add to a rising physique of proof reporting modest results of major care-based prevention and remedy of AUD, suggesting ongoing difficulties with implementation. Due to this fact, it is suggested that future analysis focuses on figuring out facilitators for implementation, together with the kind of implementation technique, and size and magnitude of intervention effectiveness.
Future analysis is required to establish limitations and facilitators of implementing primary-based care prevention of alcohol misuse within the NHS.
Assertion of curiosity
SA conducts analysis within the space of alcohol and substance misuse. No conflicts of curiosity with the paper reviewed on this weblog.
Hyperlinks
Major paper
Lee AKBobb JFRichards JE, et al. Integrating Alcohol-Associated Prevention and Therapy Into Major Care: A Cluster Randomized Implementation Trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2023;183(4):319–328. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.7083
Different references
Aira M, Kauhanen J, Larivaara P, Rautio P. Elements influencing inquiry about sufferers’ alcohol consumption by major well being care physicians: qualitative semi-structured interview research. Fam Pract. 2003 Jun;20(3):270-5. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmg307.
Anton RF, O’Malley SS, Ciraulo DA, Cisler RA, Couper D, Donovan DM, Gastfriend DR, Hosking JD, Johnson BA, LoCastro JS, Longabaugh R, Mason BJ, Mattson ME, Miller WR, Pettinati HM, Randall CL, Swift R, Weiss RD, Williams LD, Zweben A; COMBINE Research Analysis Group. Mixed pharmacotherapies and behavioral interventions for alcohol dependence: the COMBINE research: a randomized managed trial. JAMA. 2006 Might 3;295(17):2003-17. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.17.2003.
Brown J, West R, Angus C, Beard E, Brennan A, Drummond C, Hickman M, Holmes J, Kaner E, Michie S. Comparability of transient interventions in major care on smoking and extreme alcohol consumption: a inhabitants survey in England. Br J Gen Pract. 2016 Jan;66(642):e1-9. doi: 10.3399/bjgp16X683149.
Beyer F, Lynch E, Kaner E. Temporary Interventions in Major Care: an Proof Overview of Practitioner and Digital Intervention Programmes. Curr Addict Rep. 2018;5(2):265-273. doi: 10.1007/s40429-018-0198-7. Epub 2018 Might 3.
Fleming MF. Screening and transient intervention in major care settings. Alcohol Res Well being. 2004-2005;28(2):57-62.
Rapley T, Might C, Frances Kaner E. Nonetheless a troublesome enterprise? Negotiating alcohol-related issues basically apply consultations. Soc Sci Med. 2006 Nov;63(9):2418-28. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2006.05.025.
World Well being Organisation (2022) https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/element/alcohol
Picture credit
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink





